A Framework for Teaching to Diversity – Chapter 2 of U.D.L
To help us work towards our school goal of purposefully implementing the Universal Design for Learning approach to our formal planning (sometimes referred to as “Backwards by Design”, “Understanding by Design”, or “Planning With The End in Mind), my principal has provided our staff with a copy of Dr. Jennifer Katz‘s book, Teaching to Diversity: The Three-Block Model of Universal Design for Learning. As I make my way through the book, I will be summarizing my learning as a means of organizing my thoughts and getting clarification on particular ideas.

Universal Design for Learning (U.D.L.)
– What “ramps” are available to us to ensure that all of our students can
access the curriculum and gain the same experience/be actively involved
– Eight Principles for Universal Design of Instruction/Activities
1) Class Climate
– Classroom policies and practices respect diversity and include
all students
2) Interaction
– Encourage regular communication between all students and
students and yourself
– Ensure everyone is included
3) Physical Environments and Products
– Make sure that your classroom, specific activities, centres, etc
are accessible to all students in the room
4) Instructional Standards
– Have high expectations of your students and provide supports/
resources to ensure all students can meet expectations
5) Delivery Methods
– Utilize multiple teaching methods to meet the range of students
in your classroom
6) Information Resources & Technology
– Make sure that any notes, handouts, assignments, assessments
are accessible to all students
7) Feedback
– Provide students with regular, meaningful, feedback
8) Assessment
– Assess students regularly, through a variety of assessment
techniques, and change any instruction accordingly
Insights Through Brain Research
– It is very important that students are exposed to a wide-variety of
stimuli so that their brain can build the necessary neuro-pathways
to utilize that information successfully in the future
– Recognition Pathways
– Acquire factual information
– Information can be gathered through all the senses so it is
important to provide multiple learning methods so that more
recognition pathways can be built
– Strategic Pathways
– How we learn and how to represent learning
– Built when students make connections between different
concepts, practice representing information in different
ways, and problem-solve to fill in missing pieces
– Affective Pathways
– Responsible for motivation and attention
– When students are challenged and engaged to discover new
ideas they utilize their affective pathways to empower the
learning opportunity
Seven Ramps for Brain-Based Instruction
1 ) Technology
– Technology can be great for providing supports to students
but it can be negative when it requires the student to leave
the room in order to use the technology (going to a computer lab)
– Technology should be used as a support and to help students
take their learning beyond the classroom, but it should not be
the focus
2 ) Gradual Release
– Set students up so that there is a gradual release of
responsibility in the learning process
– First, the teacher demonstrates a concept and students watch
– Second, teachers and students work through a concept
together, discuss strategies, work through problems, and
practice various representations
– Third, students work independently through the concept
3 ) Flexible Grouping
– Students have opportunities to work independently, in small-groups,
and large-groups
– This allows students to demonstrate their strengths, practice skills
modelled by other students, listen to different perspectives, etc
4 ) Integrated Curriculum
– The brain remembers information best when it is connected to
prior-knowledge or experiences
– Teachers need to showcase connections between concepts and
make sure that they do not teach their subjects in isolation
– Cross-curricular opportunities are awesome for building
connections
5 ) Choice, Risk-Taking, and Safety
– If students experience too little or too few emotions, they tune out
of the learning experience
– Teachers can provide choice to help students feel confident and
more engaged in an activity
– Teachers need to help students develop their social emotional
development, as well as their academic development, to ensure
they have a successful experience
6 ) Authentic Assessment
– Assessment for learning
– Assessment as learning
– Assessment for learning
– Remember what you are assessing, are you assessing their
understanding of plant and animal cells? If so, then it doesn’t
matter what format they use to show you their understanding.
If you give a traditional test, you may only test their reading
comprehension and not their understanding of science concepts
7 ) Differentiated Instruction
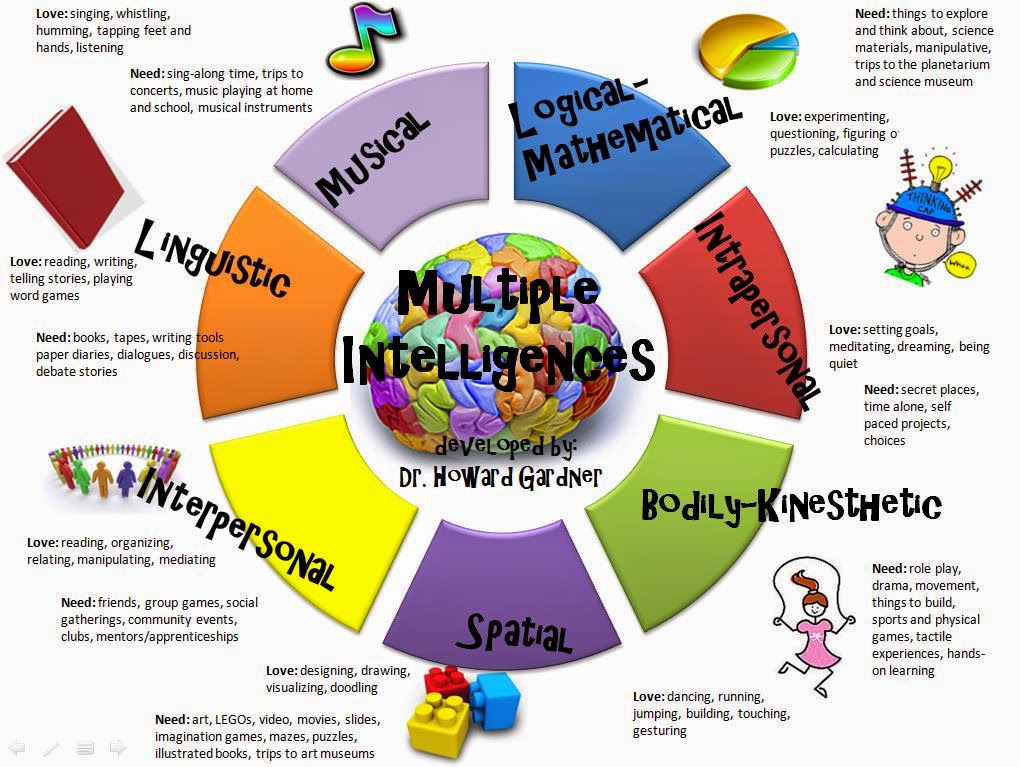
– Use multiple intelligences
 |
|
Infographic (Multiple Intelligences). (2012). Uploaded by Byanna Freund.
Available online at http://amfreund.info/2012/02/08/infographic-multiple-intelligences-2/
|
Bringing It All Together
– A three-block model was developed to put all of these ideas together
 |
| Figure 2.1 Universal Design for Learning: The Three-Block Model. (2012). Teaching to Diversity, Jennifer Katz. Page 25. |